Table of Contents
Support GPIO based IR Blaster
This functionality is available on Ubuntu.
- ODROID-C2 : Version should be 3.14.79-94 (Nov 21, 2016) or higher.
- ODROID-C1 : Version should be 3.10.104-175 (Nov 21, 2016) or higher.
- ODROID-XU3/4 : Version should be 4.9.33-42 (Jun 20, 2017) (available on kernel 3.10 with 3.10.104-126 (Nov 29, 2016))
Building and Testing an IR LED Circuit
This is a schematic example for connecting the IR LED to a GPIO output.
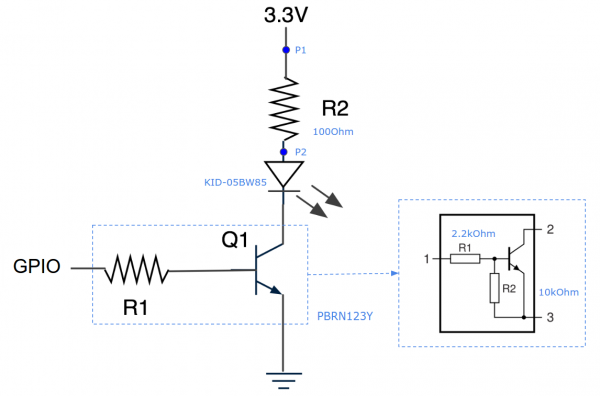
The components are not restricted to the parts and values but they can be different,
so please determine R1 and R2 values by checking the capability of IR LED and transistor specifications
based on your environment and component parts.
We use the following components for test.
- IR LED : KID-05BW85
- NPN Transistor : PBRN123Y
- R1 : None, in case of the test environment, R1 is included in the RET
- R2 : 100Ohm, in case of the test environment, the forward current is 20mA and voltage difference between P1 and P2 is 1.9V. (33Ohm - 54mA / 10Ohm - 155mA, It should be specified considering IR LED spec.)
Example for ODROID-C2 using 40pins Expansion Connectors
For example, Pin #7 (GPIO #249) is used and following instructions will be described with the GPIO value.
| LED side | Connector |
|---|---|
| VCC | Pin #1 - 3.3V Power |
| GND | Pin #6 - Ground |
| GPIO | Pin #7 - GPIOX.BIT21, GPIO #249 |
http://odroid.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=en:c2_hardware#expansion_connectors
Example for ODROID-C1 using 40pins Expansion Connectors
For example, Pin #7 (GPIO #83) is used and following instructions will be described with the GPIO value.
| LED side | Connector |
|---|---|
| VCC | Pin #1 - 3.3V Power |
| GND | Pin #6 - Ground |
| GPIO | Pin #7 - GPIO #83 |
http://odroid.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=en:c1_hardware#expansion_connectors
Example for ODROID-XU4 using 2x15 pins Expansion Connectors
For example, Pin #26 (GPIO #24) is used and following instructions will be described with the GPIO value.
| LED side | Connector |
|---|---|
| VCC | Pin #29 - 1.8V Power |
| GND | Pin #28 - Ground |
| GPIO | Pin #26 - GPIO #24 |
In case of XU4, voltage level of VDD_IO and GPIO output is 1.8V.
Supposing R2 is 10 Ohm, the actual forward current is around 40mA and voltage difference between P1 and P2 is around 400mV.
http://odroid.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=en:xu4_hardware#expansion_connectors
Install LIRC Package
$ sudo apt-get install lirc
Install LIRC package. While installing lirc, you will be asked the device type of IR receiver and transmitter.
Since we will set up later by manual, you can select None.
And for further information, please refer to the following wiki page.
http://odroid.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=en:c2_lirc
Configuring the LIRC and the driver module
LIRC Configuration
lirc_odroid module driver is already included by default but, you need to set up hardware.conf and lircd.conf first and then probe the modules with some parameters.
# sudo vi /etc/lirc/hardware.conf
Specify the kernel driver module and its node.
#Chosen IR Transmitter TRANSMITTER="odroid blaster" TRANSMITTER_MODULES="lirc_odroid lirc_dev" TRANSMITTER_DRIVER="" TRANSMITTER_DEVICE="/dev/lirc0" TRANSMITTER_SOCKET="" TRANSMITTER_LIRCD_CONF="" TRANSMITTER_LIRCD_ARGS=""
About lircd.conf, you can refer to the following link.
http://odroid.com/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=en:c2_lirc
And the name in lircd.conf will be used to specify key codes using irsend.
begin remote
name odroid
bits 16
.....
.....
Install module and Run lirc service
All necessary configuration is done, you need to install lirc_odroid module and set some parameters.
# The usage of lirc_odroid module
lirc_odroid gpio_out_pin=${gpio_number} invert=[0 or 1] softcarrier=[0 or 1]
Supposing to use Pin#7 of ODROID-C2 (GPIO #249),
# service lirc stop # modprobe lirc_dev # modprobe lirc_odroid gpio_out_pin=249 softcarrier=1 invert=1 (automatically, service lirc will be started)
Send IR code using 'irsend'
If lirc_odroid module has been loaded and lirc service is running normally, you can get the key list as following.
Please make sure the remote name is same with the description in /etc/lirc/lircd.conf.
#root@odroid64:~# irsend LIST odroid "" irsend: 0000000000009966 KEY_LEFT irsend: 000000000000837c KEY_RIGHT irsend: 00000000000053ac KEY_UP irsend: 0000000000004bb4 KEY_DOWN irsend: 000000000000738c KEY_ENTER irsend: 00000000000041be KEY_HOME irsend: 00000000000011ee KEY_MUTE irsend: 000000000000a35c KEY_MENU irsend: 00000000000059a6 KEY_BACK irsend: 000000000000817e KEY_VOLUMEDOWN irsend: 00000000000001fe KEY_VOLUMEUP irsend: 0000000000003bc4 KEY_POWER
irsend is basic LIRC program to send the key code.
# irsend SEND_ONCE odroid KEY_ENTER
Reference Configuration Files
hardware.conf
- hardware.conf
# /etc/lirc/hardware.conf # #Chosen Remote Control REMOTE="None" REMOTE_MODULES="" REMOTE_DRIVER="" REMOTE_DEVICE="" REMOTE_SOCKET="" REMOTE_LIRCD_CONF="" REMOTE_LIRCD_ARGS="" #Chosen IR Transmitter TRANSMITTER="odroid blaster" TRANSMITTER_MODULES="lirc_odroid lirc_dev" TRANSMITTER_DRIVER="" TRANSMITTER_DEVICE="/dev/lirc0" TRANSMITTER_SOCKET="" TRANSMITTER_LIRCD_CONF="" TRANSMITTER_LIRCD_ARGS="" #Disable kernel support. #Typically, lirc will disable in-kernel support for ir devices in order to #handle them internally. Set to false to prevent lirc from disabling this #in-kernel support. #DISABLE_KERNEL_SUPPORT="true" #Enable lircd START_LIRCD="true" #Don't start lircmd even if there seems to be a good config file #START_LIRCMD="false" #Try to load appropriate kernel modules LOAD_MODULES="true" # Default configuration files for your hardware if any LIRCMD_CONF="" #Forcing noninteractive reconfiguration #If lirc is to be reconfigured by an external application #that doesn't have a debconf frontend available, the noninteractive #frontend can be invoked and set to parse REMOTE and TRANSMITTER #It will then populate all other variables without any user input #If you would like to configure lirc via standard methods, be sure #to leave this set to "false" FORCE_NONINTERACTIVE_RECONFIGURATION="false" START_LIRCMD=""
lircd.conf
- lircd.conf
begin remote name odroid bits 16 flags SPACE_ENC|CONST_LENGTH eps 30 aeps 100 header 9000 4500 one 563 1688 zero 563 564 ptrail 563 pre_data_bits 16 pre_data 0x4DB2 repeat 9000 2250 gap 100000 toggle_bit_mask 0x0 begin codes KEY_LEFT 0x9966 KEY_RIGHT 0x837C KEY_UP 0x53AC KEY_DOWN 0x4BB4 KEY_ENTER 0x738C KEY_HOME 0x41BE KEY_MUTE 0x11EE KEY_MENU 0xA35C KEY_BACK 0x59A6 KEY_VOLUMEDOWN 0x817E KEY_VOLUMEUP 0x01FE KEY_POWER 0x3BC4 end codes end remote
To support both of IR Tx and Rx simultaneously
#Chosen Remote Control REMOTE="None" REMOTE_MODULES="meson-ir" REMOTE_DRIVER="" REMOTE_DEVICE="/dev/lirc0" REMOTE_SOCKET="" REMOTE_LIRCD_CONF="" REMOTE_LIRCD_ARGS="--uinput" #Chosen IR Transmitter TRANSMITTER="Home-brew (odroid gpio)" TRANSMITTER_MODULES="lirc_odroid lirc_dev" TRANSMITTER_DRIVER="" TRANSMITTER_DEVICE="/dev/lirc1" TRANSMITTER_SOCKET="" TRANSMITTER_LIRCD_CONF="" TRANSMITTER_LIRCD_ARGS="" ... ...